Determine the Format of the External Data
If you want to create a custom import mapping, you must start with a source with external data, such as an Excel file. If you do not have this, you cannot create the mapping.
You must define which columns the Excel file should contain. It is also a good idea to have actual data in the file.
- You do not yet know which fields you must import.
- The export functionality that creates the file does not yet exist.
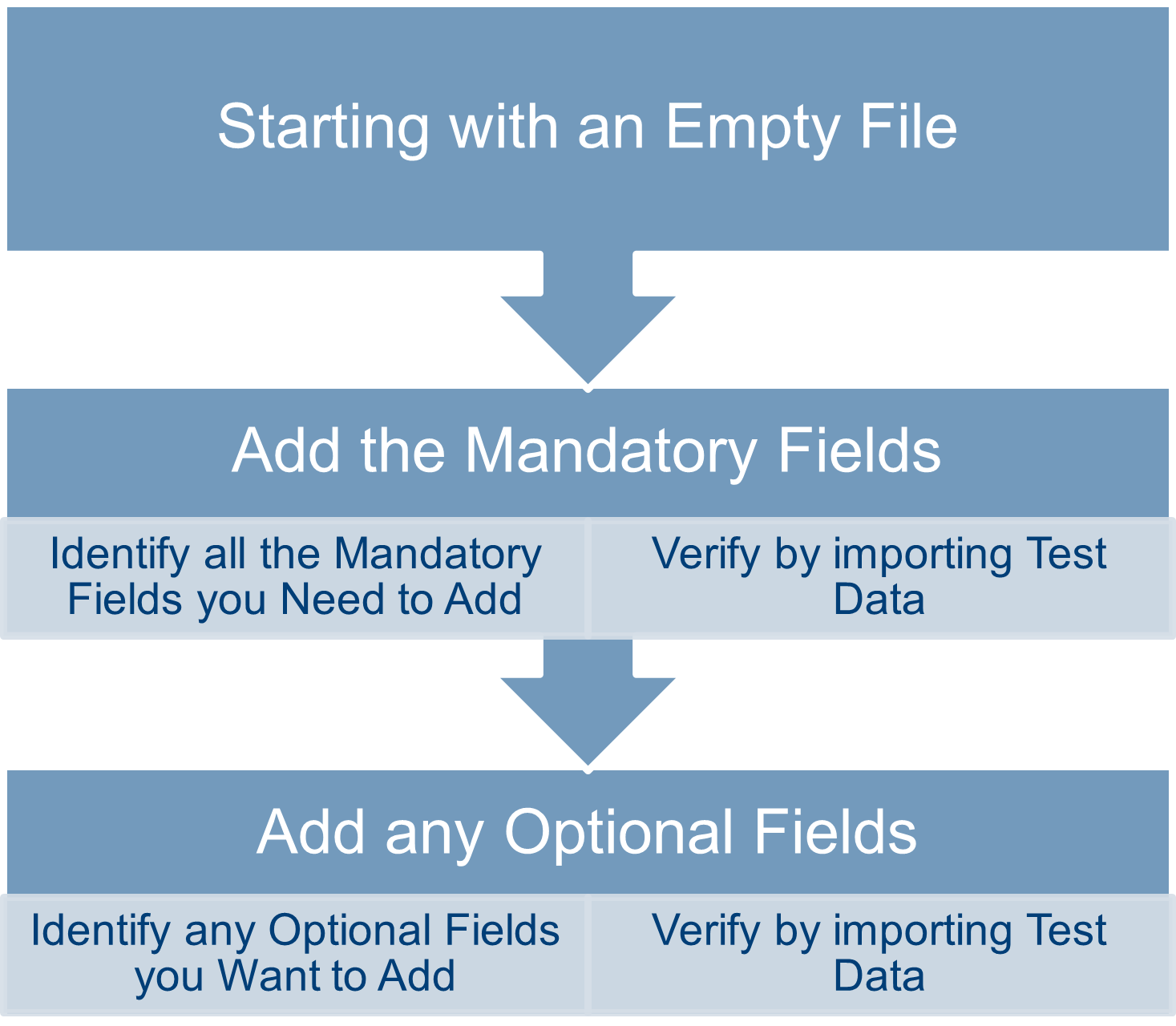
People Planner allows you to use an empty Excel file. Using an empty file, you can proceed to the point where you can identify the fields to add.
Adding New Fields
When you are in the process of defining a Custom Import Mapping, and you specify a file with external data, People Planner loads the file. People Planner does this to be able to map the fields and to show the preview data from the file.
If you decide that you need to add a new column to the file, there is no easy way to force People Planner to reread the file. Instead, you must save the incomplete Custom Import Mapping and close the editing dialog. You can then open the CustomImport Mapping again by editing it. This forces People Planner to read the file again, and it then discovers the new columns and test data.
Identifying the Mandatory Fields
Mandatory fields are recognizable by the icon. However, a few of the mandatory fields lack this icon, and the only way to identify them is to try out the import; any mandatory field that is missing results in an error message.Verifying Using Test Data
You should always verify that the Custom Import Mapping works as intended by importing some data. If you do not already have real data available, you can try to create some test data and use that.
Using test data can also be a useful tool if you are not sure about the format:
-
Numbers: Should you use decimal points or commas?
-
Dates: Should you use the "mm/dd-yyyy" or the "dd/mm-yyyy" format?